机器学习的定义如下:
Arthur Samuel (1959). Machine Learning: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
Tom Mitchell (1998) Well-posed Learning Problem: A computer program is said to learn
from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
机器学习又被划分为两类算法,
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
其它还有强化学习(reinforcement learning)和推荐系统(recommender systems)。
监督学习(Supervised learning)
we are given a data set and already know what our correct output should look like, having the idea that there is a relationship between the input and the output.
监督学习将问题分为”回归”和”分类”两类问题。前者解决连续的值的问题,后者解决离散的值的问题。例如,预测房价就是一个回归问题,而根据肿瘤的大小判断是否为恶性肿瘤则是一种分类问题。
无监督学习(Unsupervised Learning)
Unsupervised learning allows us to approach problems with little or no idea what our results should look like. We can derive structure from data where we don’t necessarily know the effect of the variables.
非监督学习是一种学习机制,你给算法大量的数据,要求它找出数据中蕴含的类型结构。在非监督学习中,数据没有属性或者标签的概念,所有的数据都是一样的,没有任何区别(而你的目标就是找出区别,并且把数据分类)。
With unsupervised learning there is no feedback based on the prediction results.
非监督学习主要可以分为聚类算法问题和非聚类算法问题两种:
Clustering Algorithm 聚类算法
将一个数据集分成几个聚类,这就是聚类算法。
典型例子是google新闻,它把成千上万的新闻聚集起来,按照每个新闻的内容分成一个一个的专题。
Cocktail Party Algorithm 鸡尾酒会算法(Non-clustering Algorithm 非聚类算法)
有一个宴会,有一屋子的人,大家都坐在一起,而且在同时说话,有许多声音混杂在一起,因为每个人都是在同一时间说话的,在这种情况下你很难听清楚你面前的人说的话。因此,比如有这样一个场景,宴会上只有两个人,同时说话, 有两个麦克风,把它们放在房间里,然后因为这两个麦克风距离这两个人的距离不同,每个麦克风都记录下了来自两个人的声音的不同组合。A的声音在第一个麦克风里的声音会响一点,B的声音在第二个麦克风里会比较响一点,因为两个麦克风的位置相对于两个说话者的位置是不同的。但每个麦克风都会录到来自两个说话者的重叠部分的声音。
鸡尾酒会算法:找出其中蕴含的分类,算法还会分离出两个被叠加到一起的音频源。
模型表示(Model Representation)
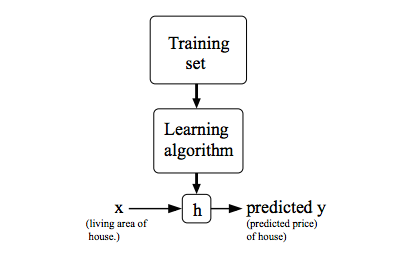
我们将训练集数据交给学习算法,将会得到一个函数,通常用h来表示,h则代表hypothesis 假设。对于函数h,输入变量x’s,得到输出y’s。
符号表示
m = Number of training examples 训练样本的数目
x′s = “input” variable / features 输入变量/特征量
y′s = “output” variable / “target” variable 输出变量/目标变量
(x,y) = one training example 某一个训练样本(泛指)
(x(i),y(i)) ith training example 第i个训练样本(特指)
Training Set: a list of m training examples (x(i),y(i));i=1,…,m
总结
吴恩达老师的机器学习入门课十分有趣,现在回看起来依然还能学到很多东西。那个时候看完一节课就忘掉了内容,知识点也没有记笔记。开博客写希望是能重新学习一次,学习原理。
代价函数(Cost Function)
We can measure the accuracy of our hypothesis function by using a cost function. This takes an average difference (actually a fancier version of an average) of all the results of the hypothesis with inputs from x′s and the actual output y′s.